An investigation of the effects of melatonin administration on biochemical parameters in rats with experimental cartilage damage Healing Effects of Melatonin on Chondral Problems
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objective: This study was intended to show the effects of melatonin (MEL) in the treatment of cartilage damage in a rat model as a novel field of application.
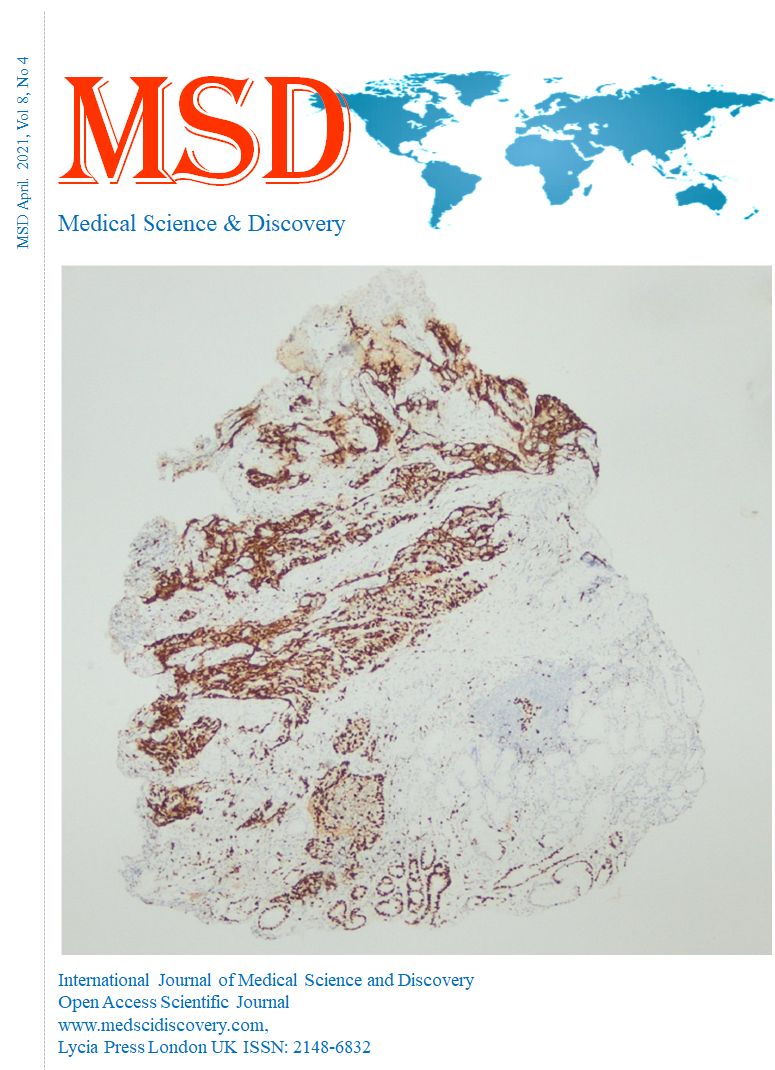
Materials and Methods: Male Sprague Dawley rats aged 3-4 months were assigned into four groups of six rats each. Group I represented the sham group. In groups 2, 3, and 4, the right knee medial meniscus was surgically destabilized. MEL was administered to groups 3 and 4 twice a week at dosages of 0.4 μg/ml and 4 μg/ml, respectively. The application continued for four weeks. Histological examinations, imaging studies [computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging], and biochemical tests [cartilage and bone turnover markers (COMP and CTX-I)] were performed.
Results: The application of MEL initiated regeneration in the damaged areas. However, cartilage repair was not observed in areas with experimental cartilage damage without MEL application. MEL-treated rats had higher T2 scores compared to Group 1 in the median femoral condyle at the 12th week (p<0.05). Serum COMP and CTX-I levels at 12 weeks were significantly higher in Group 2 compared to Group 1 (p<0.05). Serum COMP and CTX-I levels at 12 weeks were lower in groups 3 and 4, but were also significantly higher than in Group 1 (p<0.05).
Conclusion: We recommend MEL therapy for diseases related to cartilage damage. MEL seems to exert its therapeutic effect on cartilage damage through its antioxidant properties.
Downloads
Article Details
Accepted 2021-04-17
Published 2021-04-20
References
Auld F, Maschauer EL, Morrison I, Skene DJ, Riha RL. Evidence for the efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of primary adult sleep disorders. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 2017 Aug 1;34:10-22.
Faraone SV. ADHD: Non-Pharmacologic Interventions, An Issue of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America, E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2014 Oct 28.
Auld F, Maschauer EL, Morrison I, Skene DJ, Riha RL. Evidence for the efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of primary adult sleep disorders. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 2017 Aug 1;34:10-22.
British national formulary: BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 482–483. ISBN 9780857113382.
Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing Therapeutic Goods Administration. January 2011. pp. 2, 4. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
Circadin EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 31 May 2020. © European Medicines Agency
Yang W, Kang X, Qin N, Li F, Jin X, Ma Z, Qian Z, Wu S. Melatonin protects chondrocytes from impairment induced by glucocorticoids via NAD+-dependent SIRT1. Steroids. 2017 Oct 1;126:24-9.
WHO Department of Chronic Diseases and Health Promotion. Available at: http://www.who.int/chp/topics/rheumatic/en/
Osteoarthritis Initiative. Study Overview and Objectives, 2011. Available at: http://oai.epiucsf.org/datarelease/StudyOverview.asp Last accessed 4 December 2012.
Li Z, Li X, Chen C, Chan MT, Wu WK, Shen J. Melatonin inhibits nucleus pulposus (NP) cell proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling via the melatonin membrane receptors mediated PI 3K‐Akt pathway. Journal of Pineal Research. 2017 Oct;63(3):e12435.
Jahanban‐Esfahlan R, Mehrzadi S, Reiter RJ, Seidi K, Majidinia M, Baghi HB, Khatami N, Yousefi B, Sadeghpour A. Melatonin in regulation of inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: involvement of circadian clock genes. British journal of pharmacology. 2018 Aug;175(16):3230-8.
Kohen R, Nyska A. Invited review: Oxidation of biological systems: oxidative stress phenomena, antioxidants, redox reactions, and methods for their quantification. Toxicologic pathology. 2002 Oct;30(6):620-50..