Impact of selective serotonin receptor inhibitors on gastric histopathology in patients with depression Impact of selective serotonin receptor inhibitors on gastric histopathology
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objective: Antidepressant medications such as Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI) and Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRI) are used in the psychopharmacological treatment for various types conditions. This study aimed to investigate whether SSRIs and SNRIs could reduce gastric intestinal metaplasia.
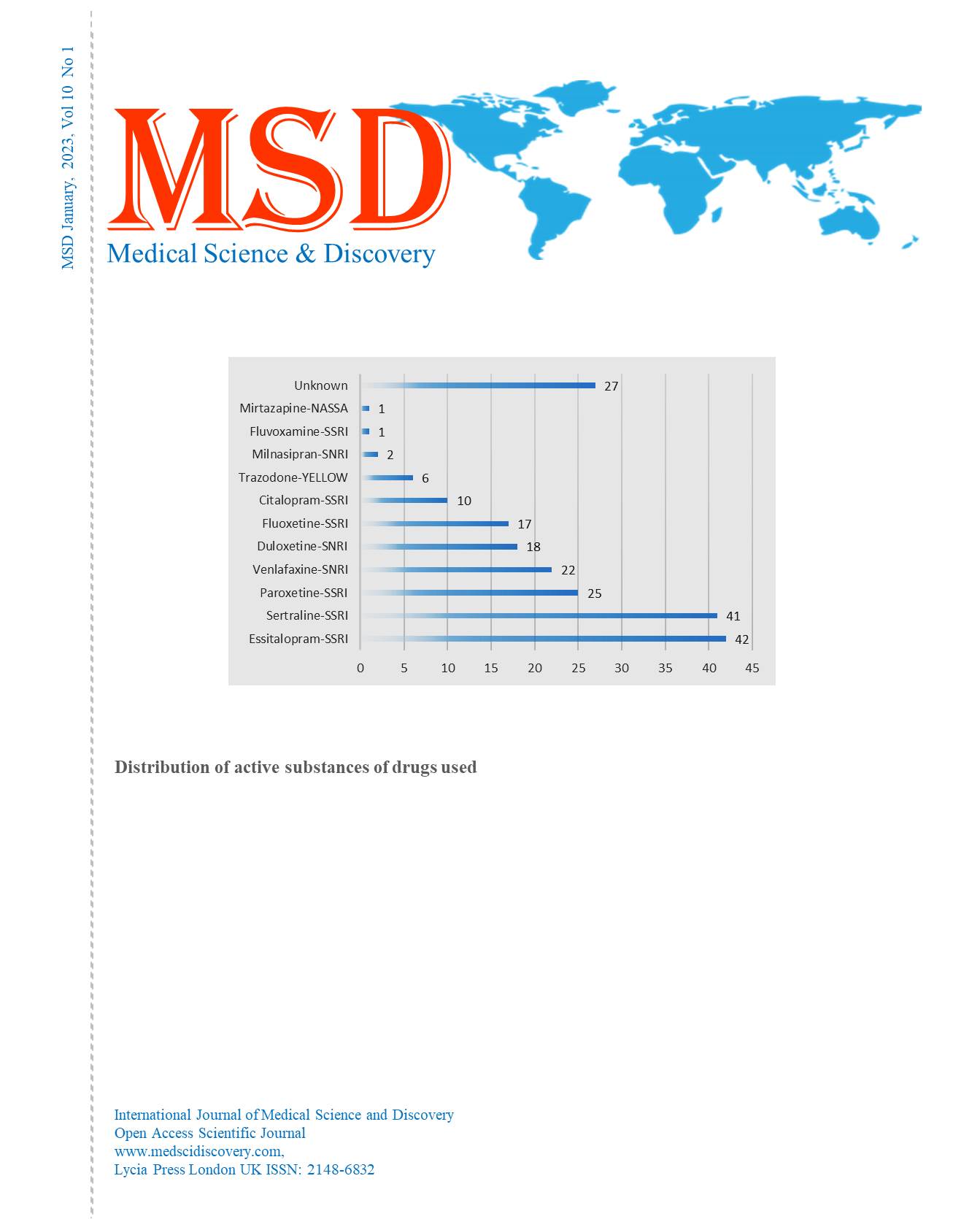
Material Methods: A total of 212 patients who underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy plus biopsy in our clinic and were using selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and other potent serotonin reuptake inhibitors were included in the study. A control group was created with a total of 230 age and gender matched patients who underwent upper gastrointestinal endoscopy plus biopsy but had no SSRI or SNRI usage. Patients’ endoscopic and pathologic findings were recorded retrospectively and compared between the groups.
Results: The patient group consisted of 180 (84.9%) male and 32 (15.1%) female patients, while the control group included 175 (76.1%) male and 55 (23.29%) female patients. There was a statistically significant difference between the groups in terms of gender (p=0.020). The rates of erythematous antral gastritis (p<0.001), peptic ulcer (p=0.019), erosive gastropathy (p=0.001) and duodenitis (p=0.002) were statistically significantly lower in the patient group compared to the control group. The rates of H.Pylori(p=0.002), intestinal metaplasia (p=0.013), neutrophil activity (acute inflammation) (p<0.001) and chronic inflammation (p<0.001) were lower in the case group compared to the control group.
Conclusion: SSRIs/SNRIs may potentially be used in treating gastrointestinal inflammation and metaplasia. However, further prospective randomised studies with larger series are needed to support our findings.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Accepted 2023-01-11
Published 2023-01-17
References
Drugs.com | Prescription Drug Information, Interactions & Side Effects. https://www.drugs.com/.
Edinoff AN, Akuly HA, Hanna TA, Carolina OO, Patti SJ, Ghaffar YA, et al. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Adverse Effects: A Narrative Review. Neurol Int. 2021;13(3):387-401. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint13030038
Antidepressant prescribing up 6% in last three months of 2020. Pharm J. June 2021. doi:10.1211/PJ.2021.1.62125.
Oliva V, Lippi M, Paci R, Fabro DL, Delvecchio G, Brambilla P, et al. Gastrointestinal side effects associated with antidepressant treatments in patients with major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021;109:110266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110266
Ormsbee I11 HS, Fondacaro’ JD. MINIREVIEW Action of Serotonin on the Gastrointestinal Tract (4201 6). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985;178(3):333-8. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-178-42016
Giroux V, Rustgi AK. Metaplasia: tissue injury adaptation and a precursor to the dysplasia-cancer sequence. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(10):594-604. PMID: 28860646
Cosmina DS, Elena MD, Daniela PO, Olga P, Maria OD, Alina B, et al. Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: Prevalence, Clinical Presentation, Endoscopic and Histological Features. Acta Medica Marisiensis. 2016;62(1):56-9. https://doi.org/10.1515/amma-2015-0061
Jencks DS, Adam JD, Borum ML, Koh JM, Stephen S, Doman DB. Overview of Current Concepts in Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Gastric Cancer. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2018;14(2):92-101. PMID: 29606921
Correa P, Piazuelo MB, Wilson KT. Pathology of gastric intestinal metaplasia: clinical implications. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(3):493-8. PMID: 20203636
Bakish D, Cavazzoni P, Chudzik J, Ravindran A, Hrdina PD. Effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on platelet serotonin parameters in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 1997;41(2):184-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3223(96)00040-6
Andrade C, Sandarsh S, Chethan KB, Nagesh KS. Serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants and abnormal bleeding: a review for clinicians and a reconsideration of mechanisms. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(12):1565-75. PMID: 201190637
Brummelte S, Mc Glanaghy E, Bonnin A, Oberlander TF. Developmental changes in serotonin signaling: Implications for early brain function, behavior and adaptation. Neuroscience. 2017;342:212-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.037
Ellero-Simatos S, Lewis JP, Georgiades A, et al. Pharmacometabolomics reveals that serotonin is implicated in aspirin response variability. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. 2014;3(7):e125. https://doi.org/10.1038/psp.2014.22
Yuet WC, Derasari D, Sivoravong J, Mason D, Jann M. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Use and Risk of Gastrointestinal and Intracranial Bleeding. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2019;119(2):102-11. https://doi.org/10.7556/jaoa.2019.016
Dall M, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB, Lassen AT, Hallas J. There is an association between selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use and uncomplicated peptic ulcers: a population-based case-control study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(11-12):1383-91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04472.x
Laursen SB, Leontiadis GI, Stanley AJ, Hallas J, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB. The use of selective serotonin receptor inhibitors (SSRIs) is not associated with increased risk of endoscopy-refractory bleeding, rebleeding or mortality in peptic ulcer bleeding. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;46(3):355-63. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14153
Gurbuz BC, Inceman HN, Aydemir M, Celtik C, Gerenli N, Zemheri E. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori among children in a training and research hospital clinic in Istanbul and comparison with Updated Sydney Classification Criteria. North Clin Istanb. 2020;7(5):499-505. PMID: 33163887
Huang RJ, Choi AY, Truong CD, Yeh MM, Hwang JH. Diagnosis and Management of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: Current Status and Future Directions. Gut Liver. 2019;13(6):596-603. PMID: 31394893
Kim N, Park YS, Cho SI, Lee HS. Prevalence and risk factors of atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia in a Korean population without significant gastroduodenal disease. Helicobacter. 2008;13(4):245-55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-5378.2008.00604.x