TNF-alpha Induces Pro-Inflammatory Factors in Colorectal Cancer Microenvironment
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objective: The tumor microenvironment has a crucial role in organizing cancer malignancy, progression, drug resistance and survival. It consists of cellular and non-cellular components. These non-cellular components such as cytokines, extracellular matrix, growth factors and metabolites are responsible for shifting the action from pro-cancer to anti-cancer effects. Twenty percent of all cancers occur in association with chronic inflammation via cytokines. Even cancers that are not caused by chronic inflammation, present high levels of cytokine expression pattern in their tumor microenvironment. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and some interleukins are characterized as pro-tumorigenic cytokines and they were involved in cancer by presenting their ability to activate the oncogenic transcription factors. The aim of this study is to evaluate the remodeling of colorectal cancer tumor microenvironment by TNF-α.
Material and Methods: TNF-α (5ng/ml) was applied to HT-29 colorectal cancer cells, then human soluble factors were determined by using Human Cytokine Group 1, 8 plex Panel (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc. USA) and Magpix Luminex instrument and xPONENT software (version 4.2, Luminex Corp, Austin, Texas, US). The results were normalized to total protein concentration estimated via Bradford assay.
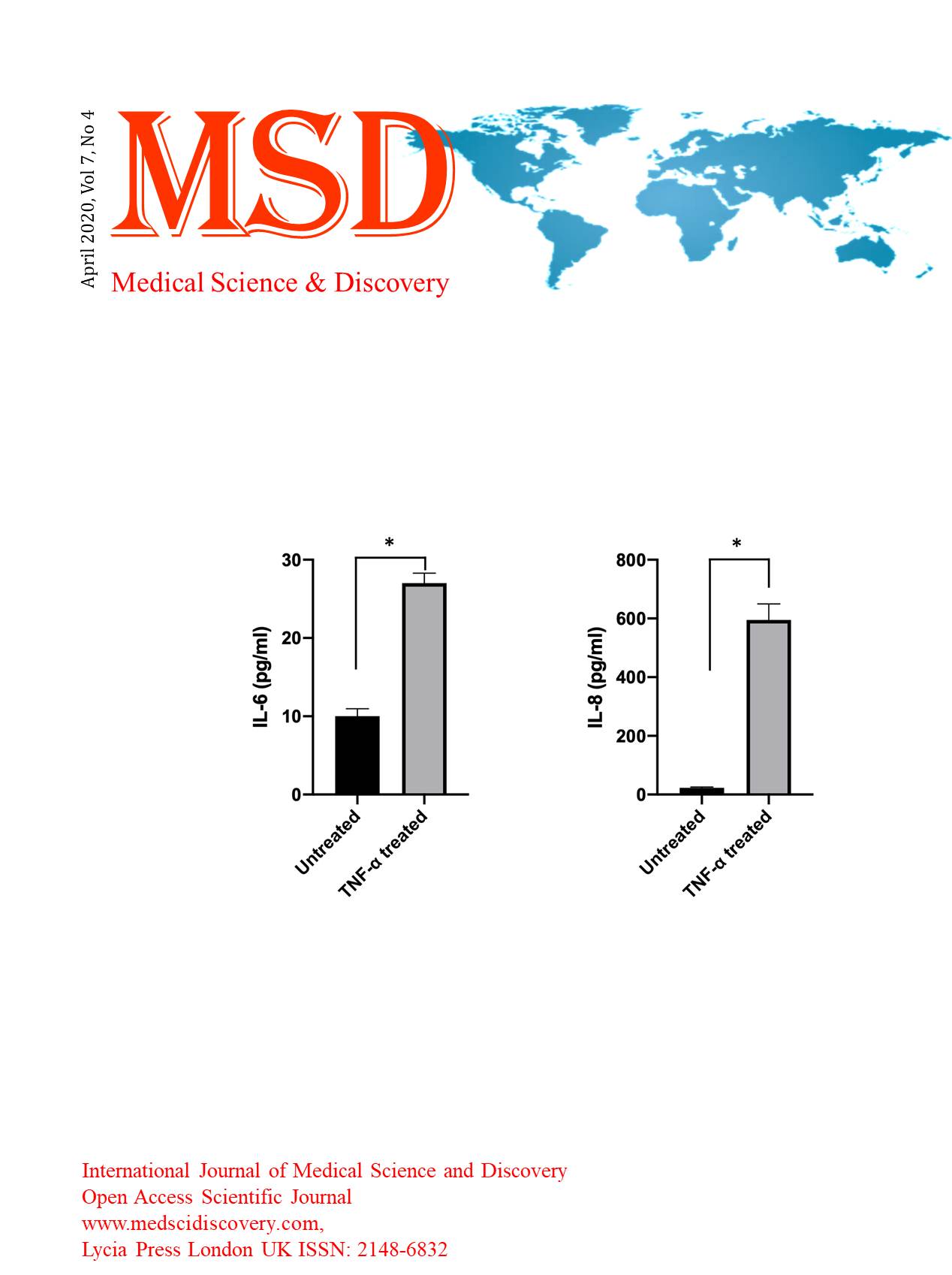
Results: Current research highlights the effect of TNF-α on the tumor microenvironment. Interleukin-6 and interleukin -8 soluble factors were higher in TNF-α treated colorectal cancer cells when compared with untreated control group.
Conclusion: The results of the study show that TNF-α is responsible for elevating the levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, which are associated with inflammation in the tumor microenvironment.
Key words: Colorectal Cancer, Tumor Microenvironment, Cytokines, TNF-α, Interleukin-6, interleukin -8
Downloads
Article Details
Accepted 2020-04-28
Published 2020-04-30
References
Patel H, Nilendu P, Jahagirdar D, Pal JK, et al. Modulating secreted components of tumor microenvironment: A masterstroke in tumor therapeutics. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018;19(1): 3–12.
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, et al. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1073-81.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, et al. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44.
Matsumoto S, Hara T, Mitsuyama K, et al. Essential Roles of IL-6 Trans-Signaling in Colonic Epithelial Cells, Induced by the IL-6/soluble-IL-6 Receptor Derived From Lamina Propria Macrophages, on the Development of Colitis-Associated Premalignant Cancer in a Murine Model J Immunol. 2010;184: 1543–51.
Ernst M, Najdovska M, Grail D, et al. STAT3 and STAT1 mediate IL-11-dependent and inflammation-associated gastric tumorigenesis in gp130 receptor mutant mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118: 1727–38.
Becker C, Fantini MC, Wirtz S, et al. IL-6 signaling promotes tumor growth in colorectal cancer. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:217–20.
Rigby RJ, Simmons JG, Greenhalgh CJ, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) limits damage-induced crypt hyper-proliferation and inflammation associated tumorigenesis in the colon. Oncogene. 2007;26:4833–41.
Popa C, Netea MG, Van Riel P. LCM, et al. The Role of TNF-alpha in Chronic Inflammatory Conditions, Intermediary Metabolism, and Cardiovascular Risk. J Lipid Res. 2007;48(4):751–62.
Kumari N, Dwarakanath, BS, Das A, Bhat AN. Role of interleukin-6 in Cancer Progression and Therapeutic Resistance. Tumor Biol. 2016;37(9):11553–72.
Bărbălan A, Streața I, Ivan ET, et al. Interleukin-8 mRNA Expression in Locally Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients. Curr Health Sci J. 2017;43(3):209–13.
Bondurant KL, Lundgreen A, Herrick JS, et al. Interleukin Genes and Associations with Colon and Rectal Cancer Risk and Overall Survival. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(4):905-15.
Janos Terzić 1, Sergei Grivennikov, Eliad Karin, Michael Karin. Inflammation and Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(6):2101-14.
Klampfer L. Cytokines, Inflammation and Colon Cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2011;11(4):451-64.
Grivennikov SI, Karin M. Inflammatory Cytokines in Cancer: Tumour Necrosis Factor and Interleukin 6 Take the Stage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):104-08.
Edwardson DW, arissenti AM, Kovala AT. Chemotherapy and Inflammatory Cytokine Signalling in Cancer Cells and the Tumour Microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1152:173-215.